As my colleague Víctor at Igalia has said before in his post, Aura was released to the Nokia Store. Miguel, Víctor and I are quite happy with the result achieved with this app, which intention was to be kind of a port of the Cheese application of the GNOME platform to be used in the N9 or N950 Nokia phones.
The apps allows you to use both cameras (front and principal) to record videos, applying a lot of funny effects (a subset of the GNOME Video Effects) and changing them during the recording. Being Nokia a Finnish company, we decided to name the app after a Finnish Cheese to both honor the GNOME Cheese application and Finland 😉
You can download the app from the Nokia Store where we already got more than 6000 downloads and 100 reviews with a quite good average rating.
You have an example recorded by me with my own phone using the Historical effect and uploaded to Youtube:
And you have even already other videos uploaded to Youtube talking about how Aura works. This one is from a brazilian guy (obrigado!) for FaixaMobi and shows more effects:
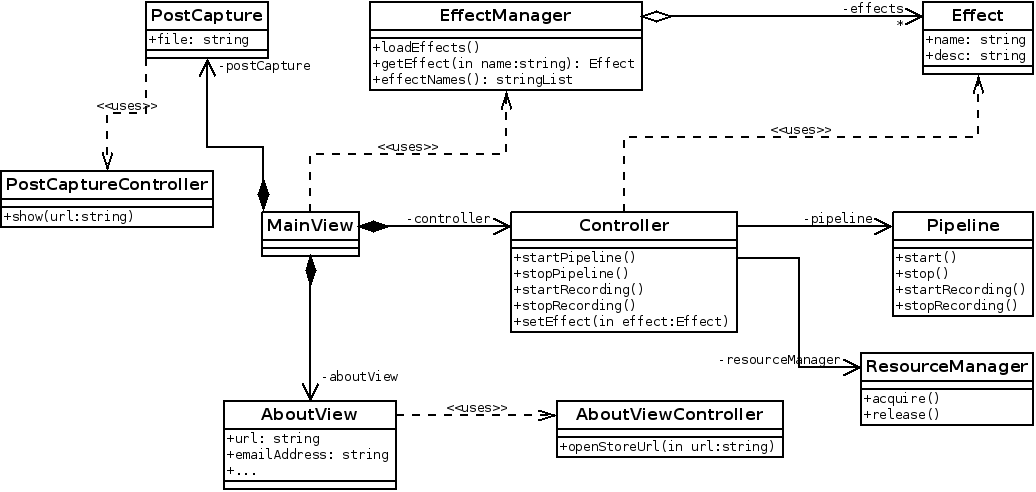
Of course, being it free sofware you can also compile it yourself with the code at GitHub and do not be afraid of contributing! The technologies we used were the camerabin element of GStreamer and Qt/QML for the interface where we have the following components:
- Main view (
aura.qml) with the main interface - Controller, which is a mixed QML/C++ object allowing to control the pipeline.
- Pipeline is a C++ object used by the controller to encapsulate the GStreamer code.
- PostCapture is also a mixed QML/C++ object that opens the gallery application to show the recorded video and gives you the oportunity of sharing it, deleting it and so on. It uses a C++ controller loaded as a singleton to the context to do some stuff that can only be done in C++. Of course, you can open Gallery yourself and the videos will show up there.
- EffectManager is a C++ class to load and manage the Effects, which is another C++ class defining how the effect must be applied.
- Effects (
Effects.qml) is a QML component to show the different effects, both software and hardware that Aura can apply. It uses the EffectManager (through the context) to load them and the Controller to apply them. - About view (
AboutView.qml) is a rework of something done by my colleage Simón Pena and adapted to be used in Aura (Kudos!). It also uses a smallAboutViewControllerto open a Nokia Store URL with the application instead of the browser. - ResourceManager is a C++ class used by the Controller to request the proper permissions to record the video.